A crossbite is a common type of malocclusion (misalignment of teeth) that can affect both children and adults. While it may not always be immediately noticeable, an untreated crossbite can lead to various oral health issues and discomfort. In this blog, we’ll cover what a crossbite is, its signs, potential effects on oral health, and the treatment options available to address it.
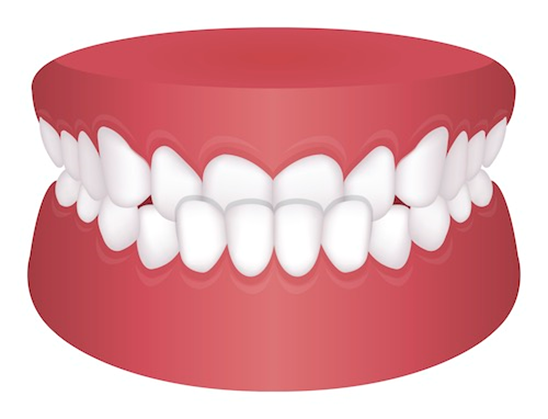
What is a Crossbite?
A crossbite occurs when the upper teeth fit inside the lower teeth when the mouth is closed, instead of slightly outside. This misalignment can affect either the front (anterior crossbite) or the back teeth (posterior crossbite) and may involve one or multiple teeth on one or both sides of the mouth.
Crossbites can be caused by genetic factors, childhood habits like thumb-sucking, or even issues with jaw development. Identifying a crossbite early allows for a simpler treatment process, especially in children whose jaws are still growing.
Signs of a Crossbite
Here are some common indicators that may suggest the presence of a crossbite:
- Uneven Wear on Teeth: Crossbites can cause teeth to wear down unevenly, leading to premature enamel erosion and tooth sensitivity.
- Jaw Pain or Clicking: The misalignment may place excess pressure on the jaw joints (TMJ), resulting in discomfort, pain, or clicking sounds during jaw movement.
- Asymmetrical Facial Appearance: Severe crossbites can affect jaw alignment, potentially causing facial asymmetry, especially in growing children.
- Frequent Biting of Cheeks or Tongue: Crossbites may cause individuals to accidentally bite the insides of their cheeks or tongue, leading to soreness and irritation.
- Difficulty Chewing or Biting: Misalignment can make biting or chewing certain foods uncomfortable or less efficient.
Recognizing these signs and addressing them early can help prevent further complications.
Effects of an Untreated Crossbite
An untreated crossbite can lead to a variety of oral health issues, including:
- Tooth Damage: Crossbites often put excess pressure on certain teeth, which can result in wear, chipping, and cracking. Over time, this can lead to enamel loss and increase the risk of tooth decay.
- Gum Recession: Misalignment often puts improper forces on the gums, which can lead to gum recession. This, in turn, increases susceptibility to periodontal disease.
- Jaw Pain and TMJ Disorders: Persistent stress on the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) can lead to TMJ disorders, which may cause chronic jaw pain, headaches, and even migraines.
- Speech and Aesthetic Issues: A severe crossbite can impact facial aesthetics and may also affect speech, making it difficult to pronounce certain sounds clearly.
- Growth Problems in Children: In growing children, an untreated crossbite can interfere with jaw development and alignment, potentially resulting in more complex dental issues later in life.
Addressing crossbites early on can help mitigate these risks and promote better long-term oral health.

Treatment Options for Crossbite
Fortunately, several effective treatment options are available for correcting crossbites. The choice of treatment depends on the patient’s age, the severity of the crossbite, and whether it affects the front or back teeth.
1. Braces
Traditional braces are one of the most effective treatments for correcting crossbites. By applying consistent pressure on the teeth, braces gradually shift them into their correct position. Braces are suitable for patients of all ages, although treatment may be faster for younger patients whose bones are still growing.
2. Clear Aligners (e.g., Invisalign)
Clear aligners offer a discreet option for mild to moderate crossbites. Custom-made to fit the patient’s teeth, aligners need to be worn for most of the day to achieve optimal results. Aligners are popular among adults and teenagers who prefer a less visible option than braces.
3. Palatal Expander
A palatal expander is typically used for children or adolescents whose jaws are still growing. This appliance gradually widens the upper jaw, creating more space for proper tooth alignment. Expanding the palate early can help prevent the need for more extensive treatments later on.
4. Jaw Surgery (Orthognathic Surgery)
In severe cases, especially in adults where the jaw has stopped growing, corrective jaw surgery may be recommended. This surgical option realigns the jaws and teeth to improve both function and appearance. It’s typically considered a last resort when other treatments are insufficient.
5. Dental Bonding or Crowns
For minor crossbites, dental bonding or crowns may be used to reshape or align individual teeth. This treatment option is generally more cosmetic and may not be effective for severe misalignments.
Conclusion
Correcting a crossbite is essential for maintaining long-term oral health and preventing potential complications. While the treatment process may vary depending on age and severity, it’s essential to consult with an orthodontist or dentist to determine the most effective option for your needs.
If you or your child show signs of a crossbite, don’t wait to seek treatment. Our team at [Your Dental Clinic’s Name] is here to provide expert guidance and customized solutions to help you achieve a healthy, aligned smile. Schedule a consultation with us today, and take the first step towards a more confident and comfortable smile!
